TAUGHT IN ITALIAN AND ENGLISH – LOCATION ROME OR MILAN ❯
The signs all around you.
You will play a key role in all of the visual communication projects, from publishing to unconventional marketing, from corporate identity to advertising, from signposting to promotions.
Qualification:
First Level Academic Diploma, equivalent to a Bachelor’s degree
Duration:
3 years, full time
Language:
Italian and English
Credits:
180 ECT
Location of attendance:
Rome or Milan
Requirements:
Italian students
High school diploma
International students
Valid High School Diploma for the Italian Higher Education System
B2 Certificate of the language in which the course is held
Upon admission non UE students are subject to fulfill the procedure for obtaining the student VISA
Field:
Visual communication, publishing, corporate identity, advertising.
Main subjects:
Graphic Design, Web Design, Copywriting, Packaging, Publication design
Future careers:
Art Direction, Copywriting, Graphic Design, Illustration, Advertising, Corporate Identity, Publication design, Web design, Social media
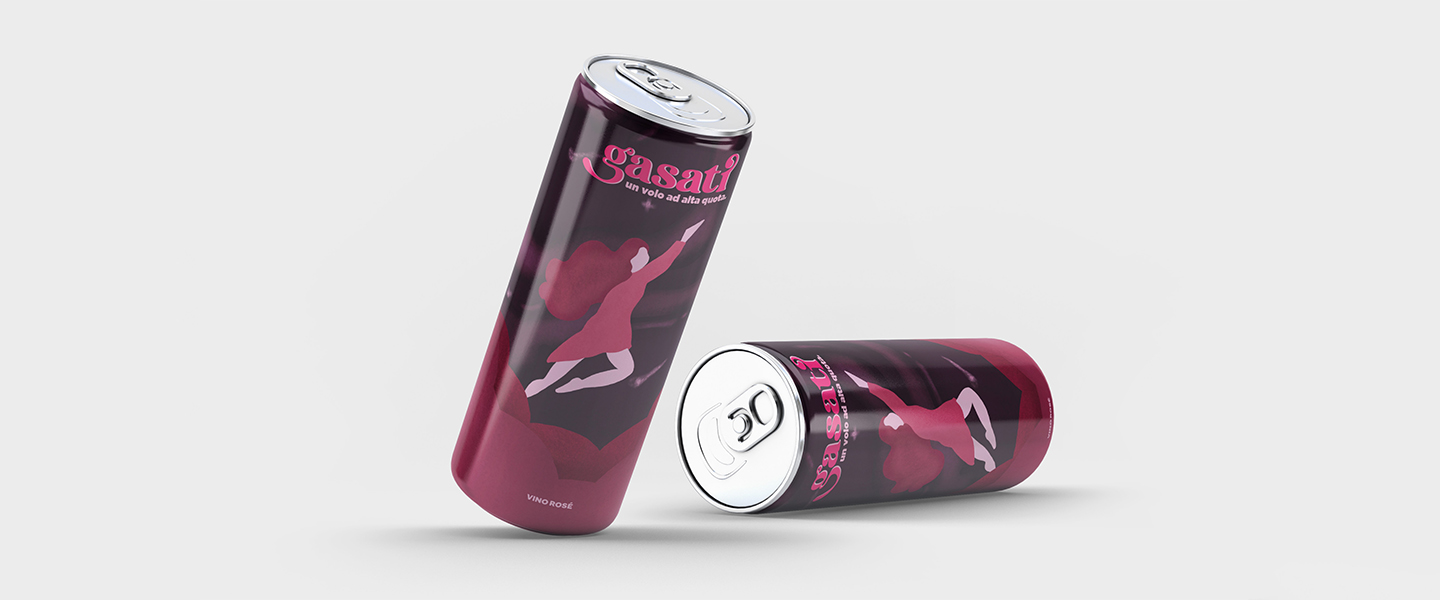
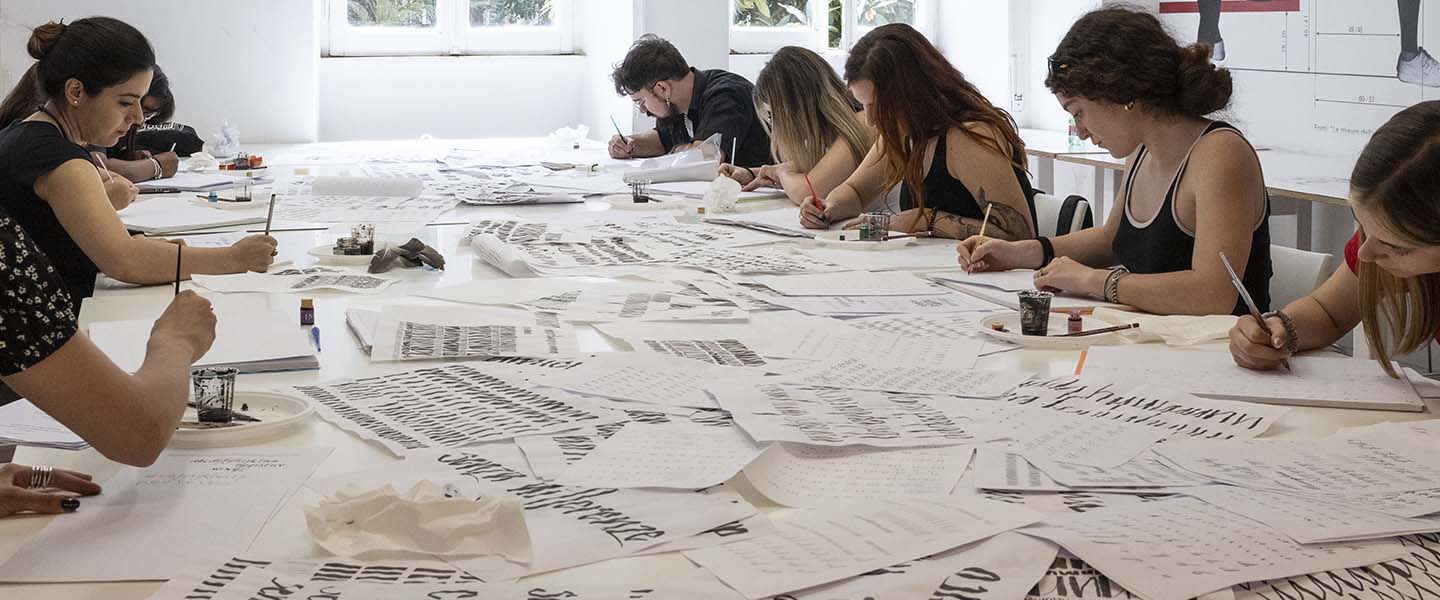
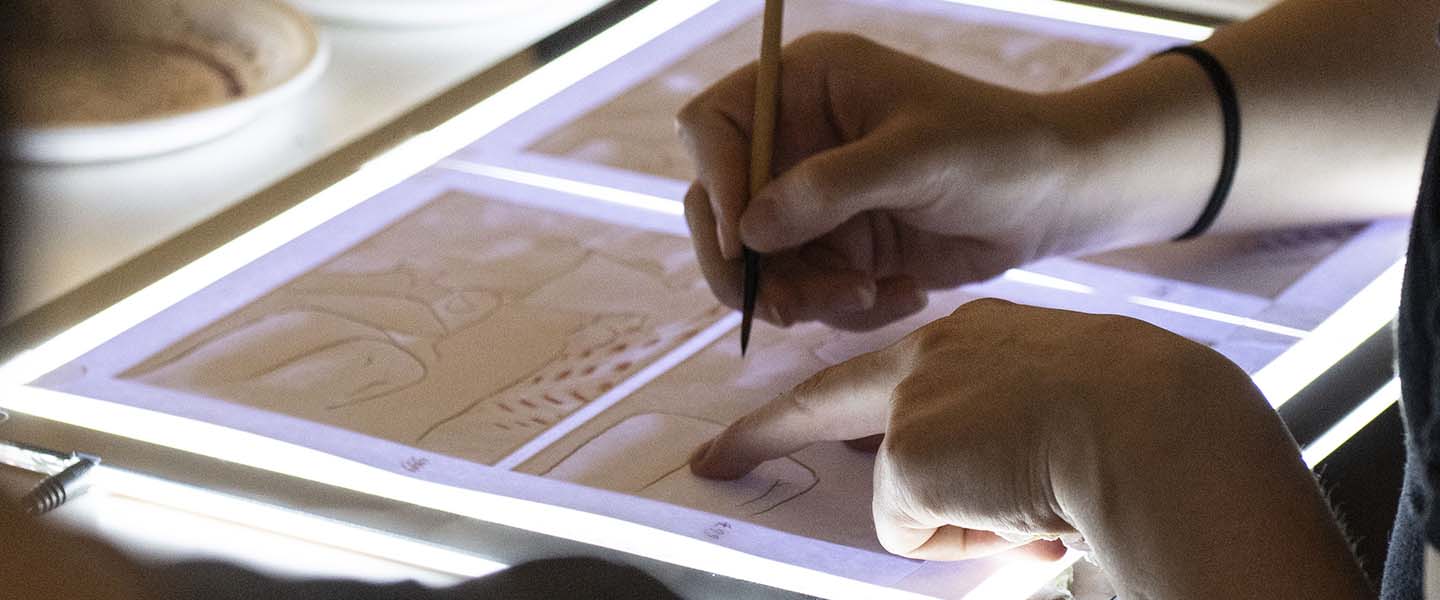
The Graphic Designer plays a key role in all projects that involve visual communication. From publishing to packaging, corporate identity to exhibits, signage to advertising. Graphic Design is a multidisciplinary profession that combines various elements of communication (signs, fonts, colours and images) to define forms of expression that must always be original and contemporary. RUFA Graphic Design graduates tackle this job market thanks to the many skills they acquired during the programme they attended at the Academy, which covers the many different aspects of visual communication. Graduates are trained in art history and publishing and have the ability to work with traditional graphics techniques as well as multimedia. Having acquired a thorough knowledge of graphics and photography, as well as of the current technologies and those of the future, RUFA graduates possess the ability to implement projects related to institutional identity, brand image, web design, wayfinding, and advertising. The profile of RUFA graduates is that of visual designers that can work in many scenarios: from independent professional practice to working within advertising agencies, public institutions, and companies.
The Academic Bachelor of Arts is equivalent to a University Bachelor’s Degree.
*All lessons include mandatory attendance at RUFA’s locations.
Coordinator: Stefano Cipolla
Tutor: Italian Luigi Iacobelli – English Francesco Paolo Incantalupo
Lecturers: Elisa Abbadessa, Agnese Angelini, Maria Pina Bentivenga, Paolo Buonaiuto, Emanuele Cappelli, Andrea Cavallari, Stefano Compagnucci, Francesco Fidani, Genny Di Bert, Giulio Fermetti, Emanuele Frasca, Alessandra Giacomelli, Alessandro Gori, Luigi Iacobelli, Guido Lombardo, Massimiliano Napoli, Antonio Pace, Enrico Parisio, Harald Pizzinini, Christian Rizzo, Lucia Sforza, Claudio Spuri, Andrea Vendetti, Livia Massaccesi, Fabrizio Matteo Rossi, Caterina Di Rienzo, Malica Worms, Fabrizio Crollari, Cinzia Capparelli, Luigi Pierantoni, Francesco Incantalupo, Davide Luccini, Giulia Boccarossa, Roberta De Cristofaro, Gaia Formigari, Andrea Vendetti, Alessandra Giacomelli, Stefano Mavilio, Rosario Di Vincenzo, Gabriele Stabile, Marco Antonutti, Irene Rinaldi, Fabio Mario Rizzotti, Stefano Perrone, Silvia Sfligiotti, Simone Santilli.
BROCHURE DOWNLOADPROGRAMME REGULATIONS
LOOK AT GRAPHIC DESIGN STUDENTS’ PROJECTS
ASK MORE INFO ABOUT THE COURSE
BACHELOR OF ARTS PROGRAMME IN GRAPHIC DESIGN
Suggested study plan – Mandatory attendance at RUFA locations in Rome
| YEAR | SUBJECT | ECTS |
|---|---|---|
| I YEAR |
Technical drawing and project design
Useful techniques and tools for creating the creative and operational aspects of your graphic work. The objectives are to sharpen the logical-design skills of the students by using geometry and composition and to teach them how to create a brand, from the initial phase to construction, up to the use of the brand manual.
| 10 |
|
Computer graphics
Basic techniques and tools: software for the management and creation of an editorial layout; software for managing files, vector and picture images; software for managing print and interactive files; software for designing graphic interfaces and user flows.
| 10 | |
|
History of printing and publishing
Basic knowledge of the history of graphic design. Its various forms and meanings developed over time: from Gutenberg, to the twentieth century, to the twenty-first century. The production and way of thinking of the major key players of each period will be studied in-depth, while focusing on the technical innovations that are impulses necessary for creative thinking.
| 8 | |
|
Graphic design 1
Graphic design: history of visual communication to acquire theoretical-critical foundations, practical phase to acquire knowledge and create the concepts related to typeface, composition, visual and layout.
| 12 | |
|
Photography 1
The foundations of the history of photography through the study of images and the authors who created them. Practical exercises: setting up the camera and artificial lighting. The light room and the connections with the dark room. The new possibilities that development, post production and editing software offer.
| 8 | |
| An elective subject to be chosen between: | ||
|
Semiotics of art
The Sign, the Interpretation, the Text and the Image are the main themes and interpretative tools of semiotics. Analysis of the art world: painting, sculpture and architecture, up to the most modern forms of digital art.
| 6 | |
|
Illustration
In-depth study of the history of illustration, design of the drawn image, manual practice through art techniques, up to the creation of the student’s own sketch book.
| 6 | |
| Elective educational activities | 6 | |
| II YEAR |
Design methodology
Management of the processes and practices related to the visual communication design. Students will become aware and independent when dealing with graphic design culture. Identification of the methodologies that are typical of the various fields of graphic design (which can be seen in structuring and problem solving), both from a theoretical and practical point of view. Given a specific theme as a case study, development of a design process capable of guaranteeing a high quality result both on in theory and practice.
| 6 |
|
History of contemporary art
Study of the moments and protagonists of the phenomenology of art. Among them: classical Greek art (Polykleitos' balance), paleochristian art, the anthropocentrism of the 1400s, Baroque, Impressionism and Avant-garde of the 1900s.
| 6 | |
|
Graphic design 2
Learning design methodologies and theoretical and practical tools to communicate complex concepts. Communication of an event / exhibition through which students will try their hand at various assigned themes. In-depth study of light and color in the field of physics, chemistry and neuroscience applied to graphic design.
| 12 | |
|
Web design
Study of the methodology and operational tools for designing and creating websites: technologies, rules, limits and state-of-the-art possibilities. Web design, content and site map, wireframe and mockup, setup for the development based on Wordpress with a predefined template, using HTML and CSS languages and developing the knowledge of CSS3 animations. Planning, design and development of a responsive website.
| 8 | |
|
Features of publication design
Theoretical and practical teaching of the basic notions related to the layout of any type of editorial project. Preparation for any type of production, print and digital.
| 8 | |
|
Photography 2
In-depth study of the photographic language, from the lexicon to the contemporary grammar. The main objective is the development of the author’s voice, intended as a distinctive mark and a tool for effective market positioning. Design thinking applied to photography will allow the student to create increasingly complex projects for images at the service of the contemporary visual field; tackle and manage the use of the Photography in contemporary, classic and digital media.
| 6 | |
|
Copywriting 1
Build concepts, images and persuasion mechanisms through words. Communicating to make products and ideas real, known, desirable. The classes include theory, practical exercises and the continuous and constant creation of solid and feasible concept strategies. The course is held in collaboration with other methodological subjects.
| 4 | |
|
Techniques and technologies for graphic design
Through a theoretical program, the course intends to present and bring to the attention of the student the range of different printing and setting up techniques and technologies, connected with the various materials, that regard the physical artefacts related to the profession of the visual designer.
| 6 | |
| Elective educational activities | 4 | |
| III YEAR |
Mass media theory and methods
The scene of broad-based communication: useful tools to draw a map of the present and to consciously and critically create a personal work. Analysis of the anthropological transformation of our time that adds value to communication and the imagination, with a focus on the knowledge worker.
| 6 |
|
Graphic design 3
Development of design skills with a dynamic and strategic approach: from the conception to the creation of a visual system with an impactful message. Ability to face, interact and control the emerging means of communication, as well as the conventional ones, and use them in relation to the target. Study of advertising: from the concept to the communication channels, up to the layout and composition rules. Creation of an advertising campaign.
| 12 | |
|
Packaging
History of packaging design and focus on the profession of the packaging designer. Study of the functional, aesthetic and semantic aspects of packaging, materials, standards and design details for cardboard packaging. Analysis of geometric shapes, paying particular attention to the transition from the two-dimensional to the three-dimensional world. Communication: shape, materials and color. Practical procedures for presenting the project.
| 6 | |
|
Copywriting 2
Reinforcement of the concepts learned, that are applied to broader communication campaigns and projects, also in collaboration with the other design subjects. The course aims to adequately prepare students to enter the job market.
| 4 | |
|
Digital animation techniques
First approach to animation: technical tools and creative skills for the creation of animated graphics and motion graphics products. Learning and use of software for the creation of effects, photo editing, graphic design; arriving to the final project through animation, compositing and rendering.
| 6 | |
|
Digital modeling techniques
Two-dimensional drawing and three-dimensional modeling techniques with specific software. File management and document exchange between 3D and architecture software. Features of the software to study lights and materials to simulate reality through the creation of the photographic image.
| 6 | |
|
Computer technologies
Generative design and the Creative Coder professional: integration of the visual communication skills with those of programming. Parametric design: union of mathematics and creativity.
| 4 | |
|
English
In-depth study of themes and topics related to the art field through the use of different vocabulary and styles to improve the students’ communication skills in English.
| 4 | |
| Further language and interpersonal skills, internships, etc. | 4 | |
| Thesis | 8 | |
| Total Credits | 180 |
CREDITS
Foto slider: Gioia D’Innocenti – Anna Piffer, Gaia Formigari – Giulia Gatta – Francesco Paolo Incantalupo – Fabio La Gattuta – Gabriele Minotti, Collettivo, Giulia Gatta, Roberta Cianci.
Partner